Phases of mitosis
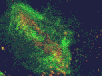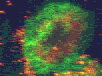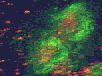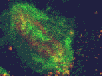
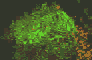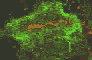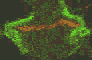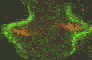
Cytokinetic complex viewed with confocal microscopy
Figures 1 through 6 illustrate the stages of mitosis in onion (Allium cepa) as viewed with light microscopy.
1 Interphase: Chromatin of chromosomes is mostly in a decondensed form, and active in transcription.
2 Prophase: Chromatin starts to condense, the spindle begins to appear, and by the end of prophase, the nuclear envelope and nucleoli have disintegrated.
3 Metaphase: Chromosomes move along the spindle microtubules in the equatorial plane of the spindle, and so-called metaphase plate of chromosomes is formed. At the end of metaphase, chromosomes consisting each of two chromatids gradually align with sister chromatids at opposite sides of the interphase pole.
4 Anaphase: The sets of sister chromatids are moved toward the poles. The poles may also separate.
5 Telophase: Chromosomes reach the spindle poles, the nuclear envelope is restored, and the spindle disappears. A cytokinetic complex of phragmoplast fibers and cell plate is formed in the equatorial plane between sister nuclei.
6 Cytokinesis: The cell plate growing centrifugally reaches the parental wall and becomes the part of the primary wall. The two new daughter cells enter interphase and the nucleoli are restored.
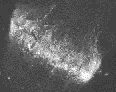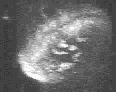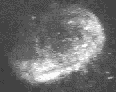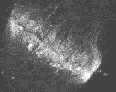
The three animated figures illustrate views of the spindle apparatus, phragmoplast microtubules, and cell plate as seen using confocal fluorescence light microscopy. The illustration on the right shows the expansion of the cytokinetic apparatus in which the phragmoplast microtubules are shown in green, and the cell plate (with presumptive callose deposits) is shown in orange. The center animation shows a tilted 3-D reconstructed cytokinetic apparatus in which the weaker orange signal in the center of the cell plate indicates the replacement of one polysaccharide by another, primarily cellulose. The monochrome rotating image at the left shows the cell plate suspended by the phragmoplast. Light deposits are believed to be callose. There is a gap between the microtubules of the upper and lower phragmoplast halves. It is at this gap where the cell plate is found.

Illustration from: http://biology.nebrwesleyan.edu/benham/mitosis/